Western Digital (WD) portable hard drives are really helpful. They offer high capacity storage, universal connectivity and are also compatible with USB 3.0 and 2.0.
If you want the WD external hard drive to work on your Mac or PC, you need to format it first. So, if you are looking for how to format your WD drive, you are on the right page. Here, we provide a step by step guide on the same.
Securing your data
Once the formatting process begins, all the data on the drive will be lost. Therefore, you will have to extract or back up your data first before you start the process.
File system formats available in Disk Utility on Mac. Disk Utility on Mac supports several file system formats: Apple File System (APFS): The file system used by macOS 10.13 or later. Mac OS Extended: The file system used by macOS 10.12 or earlier. MS-DOS (FAT) and ExFAT: File systems that are compatible with Windows. Open Disk Utility for me.
- Open Disk Management, the hard drive manager included with all versions of Windows.
- Select Disk Utility; Click on the drive with the WD label in the left pane of the Disk Utility. Click on Erase in the Disk Utility file menu. The Erase dialogue window appears. Select the Volume Format drop-down list; Choose MS-DOS (FAT)or ex-FAT File System. Click on the Erase button then wait a few minutes and let the macOS erase data on the.
- Launch Disk Utility. Either head to Applications Utilities, or tap Command + Space and start typing.
- NTFS: As the default file system in Windows, it can only read by Mac OS, writing to it is not available. Luckily, there are third-party tools to help you do so. Part 2: Format External Hard Drive for Mac with Disk Utility. Formatting an external hard drive would erase everything on it.
You can do that by copying your files to a new location one by one. If the data to be transferred is massive, then you should use a professional back up software (e.g EaseUS Todo Backup).
Read Also:How to fix itunes error 9039
Formatting your WD hard drive for Mac
Formatting your drive to FAT32 or exFAT is easier using Mac’s built-in Disk Utility. Below are the steps for the process.
- Connect your WD hard drive to your Mac computer.
- If your driver doesn’t turn up, navigate to Finder then select Preferences.
- In the small window that appears, check the boxes next to Hard Disks and External Disks. Your WD external hard drive should now be visible on your screen.
- Double-click on the driver icon that appears on your desktop.
- Click on Applications from the left pane
- Go to Utilities
- Select Disk Utility
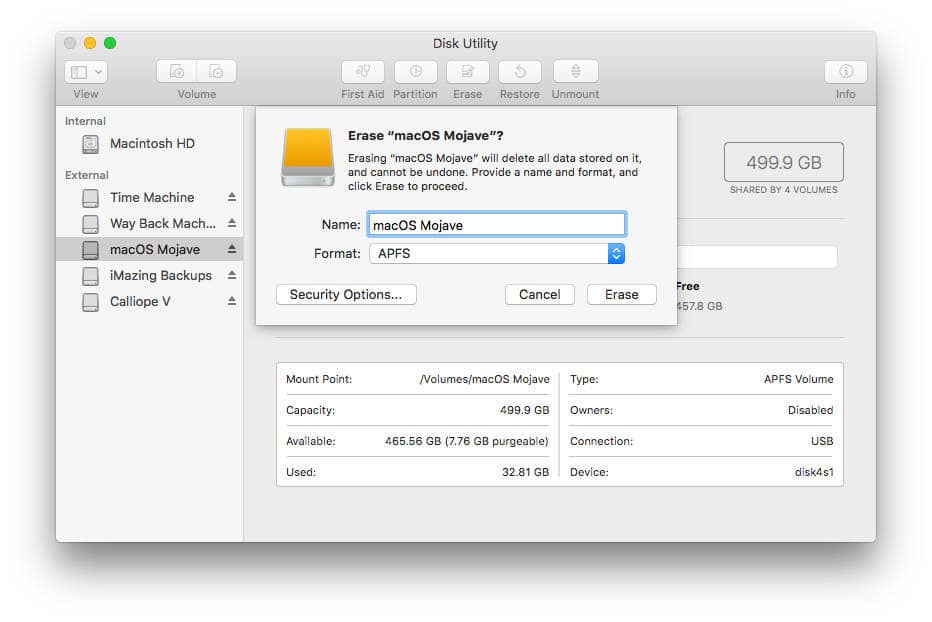
- Click on the drive with the WD label in the left pane of the Disk Utility.
- Click on Erase in the Disk Utility file menu. The Erase dialogue window appears.
- Select the Volume Format drop-down list
- Choose MS-DOS (FAT)or ex-FAT File System.
- Click on the Erase button then wait a few minutes and let the macOS erase data on the drive.
- Reformat the drive by FAT32 or ex-FAT
- Once formatting is complete, you can use the drive in your MacOS or OS X as a regular hard drive.
Note: ex-FAT is a better choice for formatting your WD on Mac.
Read Also: How to delete Google Drive from Mac
Formatting your WD hard drive for PC
Below are the steps to follow when formatting the WD Drive for Mac.
Format Hard Drive Windows 10
- Connect your WD hard drive to your Windows PC
- Click on the Start button and select This PC. A new Windows Explorer window opens.
- Right-click on the icon assigned to the WD Drive.
- Click on Format in the pop-up menu.
- Select the File System from the drop-down list then choose either ex-FAT or FAT32
- Type a name in the Volume Label This is the name that will represent your drive when you connect it with your PC or Mac.
- Select the Quick Format option then click on Start.
- Wait for a few minutes for the process to complete. After successful formatting, you can then save or move files to it.
Conclusion
Hopefully, the steps above will enable you format your WD external hard drive for Mac successfully. Should you encounter any problem with the same, let us know in the comments section.
Read Also: How to add Google Drive to Mac Finder
Disk Utility User Guide
Disk Utility on Mac supports several file system formats:
Apple File System (APFS): The file system used by macOS 10.13 or later.
Mac OS Extended: The file system used by macOS 10.12 or earlier.
MS-DOS (FAT) and ExFAT: File systems that are compatible with Windows.
Apple File System (APFS)
Apple File System (APFS), the default file system for Mac computers using macOS 10.13 or later, features strong encryption, space sharing, snapshots, fast directory sizing, and improved file system fundamentals. While APFS is optimized for the Flash/SSD storage used in recent Mac computers, it can also be used with older systems with traditional hard disk drives (HDD) and external, direct-attached storage. macOS 10.13 or later supports APFS for both bootable and data volumes.
APFS allocates disk space within a container on demand. The disk’s free space is shared and can be allocated to any of the individual volumes in the container as needed. If desired, you can specify reserve and quota sizes for each volume. Each volume uses only part of the overall container, so the available space is the total size of the container, minus the size of all the volumes in the container.
Choose one of the following APFS formats for Mac computers using macOS 10.13 or later.
APFS: Uses the APFS format.
APFS (Encrypted): Uses the APFS format and encrypts the volume.
APFS (Case-sensitive): Uses the APFS format and is case-sensitive to file and folder names. For example, folders named “Homework” and “HOMEWORK” are two different folders.
APFS (Case-sensitive, Encrypted): Uses the APFS format, is case-sensitive to file and folder names, and encrypts the volume. For example, folders named “Homework” and “HOMEWORK” are two different folders.
You can easily add or delete volumes in APFS containers. Each volume within an APFS container can have its own APFS format—APFS, APFS (Encrypted), APFS (Case-sensitive), or APFS (Case-sensitive, Encrypted).
Mac OS Extended
Format Hard Disk For Mac And Pc
Choose one of the following Mac OS Extended file system formats for compatibility with Mac computers using macOS 10.12 or earlier.
Mac OS Extended (Journaled): Uses the Mac format (Journaled HFS Plus) to protect the integrity of the hierarchical file system.
Mac OS Extended (Journaled, Encrypted): Uses the Mac format, requires a password, and encrypts the partition.
Mac OS Extended (Case-sensitive, Journaled): Uses the Mac format and is case-sensitive to folder names. For example, folders named “Homework” and “HOMEWORK” are two different folders.
Mac OS Extended (Case-sensitive, Journaled, Encrypted): Uses the Mac format, is case-sensitive to folder names, requires a password, and encrypts the partition.
Windows-compatible formats
Choose one of the following Windows-compatible file system formats if you are formatting a disk to use with Windows.
MS-DOS (FAT): Use for Windows volumes that are 32 GB or less.
ExFAT: Use for Windows volumes that are over 32 GB.
